Client Credentials Grant
This grant is suitable for machine-to-machine communication where the application is the owner of the access token. This means that you store your OAuth client credentials on your machine (server) and users of your application would make requests through your server.
Warning
Always make sure only your server has access to your client credentials or access token.
Flow
The flow of the Client Credentials grant is fairly simple. You use your client credentials to request an access token from the authentication server and then use that access token in your requests to the API server. A more in depth explanation follows below.
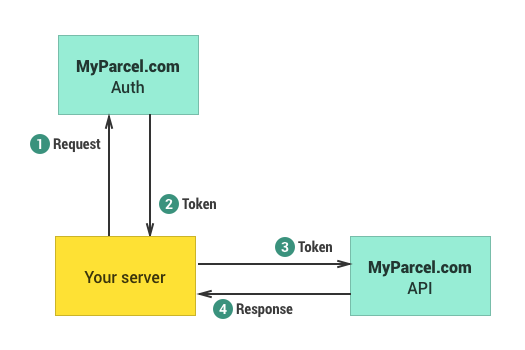
The client credentials authentication flow
1. Requesting an access token
Send a POST request to https://auth.myparcel.com/access-token or https://auth.sandbox.myparcel.com/access-token. The body must contain the following:
grant_typewith the valueclient_credentialsclient_idwith the client id as provided by MyParcel.comclient_secretwith the client secret as provided by MyParcel.comscopewith one or more scopes separated by spaces, or a*to include all scopes available to your user
Don’t forget to set the Content-Type header to application/json.
For example:
POST /access-token HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
{
"grant_type": "client_credentials",
"client_id": "b4460113-f097-49ae-9225-f741a7bf07ed",
"client_secret": "QgKgOXOwCvffUbMJKD4Lu21sZAmvw1pHGpKv1Zb6OdXBn2rkDLcyKz0JYSsFitIw",
"scope": "*"
}
2. Response with new access token
The authentication server will respond with the following body:
token_typewith the valueBearerexpires_inwith an integer representing the time to live (TTL) of the access token (in seconds)access_tokenthe access token itself
For example:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 86400,
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJuYW1lIjoiSm9obiBEb2UiLCJhZG1pbiI6dHJ1ZX0.OLvs36KmqB9cmsUrMpUutfhV52_iSz4bQMYJjkI_TLQ"
}
You can now store this access token on your system to be attached to all MyParcel.com API calls.
3. Making a request to the MyParcel.com API
To make a request to the MyParcel.com API you have to add your access token to the request. You can do this by setting the access token as the Bearer token in the Authorization header.
For example:
POST /shipments HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJuYW1lIjoiSm9obiBEb2UiLCJhZG1pbiI6dHJ1ZX0.OLvs36KmqB9cmsUrMpUutfhV52_iSz4bQMYJjkI_TLQ
Content-Type: application/vnd.api+json
All requests to the MyParcel.com API with an expired or otherwise invalid access token will be rejected. A convenient way to make sure you have an access token that has not expired, is to let the server periodically request a new access token before the previous one expires. The overlap between the different tokens will not cause a problem with running requests.
The server response
When using a valid token, the server will just give the expected response.
Tip
Always check the response for an authentication error. If for some reason your server has not retrieved a new access token yet, or your access token was revoked, you don’t want the request to fail. Just check for the error, fire a separate job to fetch the new token, and attach the new token to all pending requests.
Expired access token
Another way to handle expired access tokens (aside from periodically requesting a new one) is to queue the incoming requests when your application notices that the access token has expired. Below is an example flow of how you could set this up.
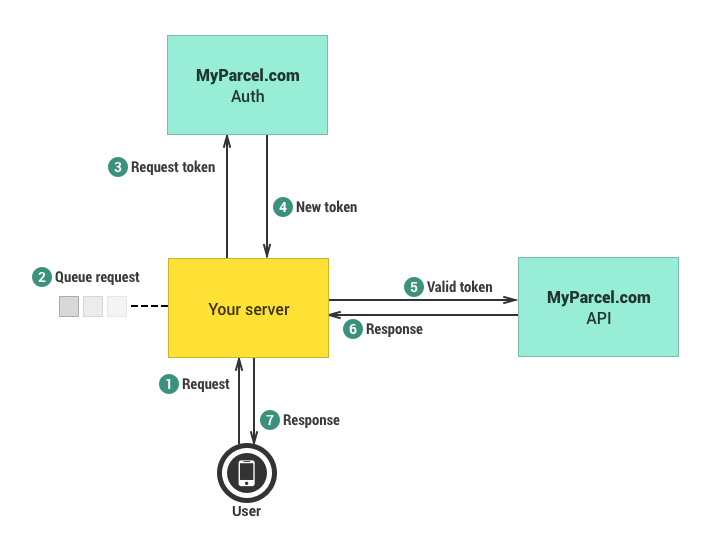
The client credentials queue flow
Since the access token is a JSON Web Token (JWT), you can simply parse it with your favourite JWT library and get the exact UNIX timestamp when the access token expires. This means that you could queue your requests either on the user’s device (step 1) or on your server (step 2) while a side job requests a new access token. When the new access token is received by the server it can be attached to all queued requests before they are executed.
Note
While you can requests access tokens more often than only just before it expires, this is not advised. Your requests will take longer to process if it has to authenticate on every request. Aside from that, your server would also have to make more requests than necessary, increasing its load.